Shin Splints
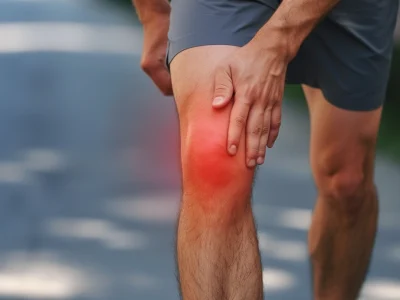
Shin splints or Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome (MTSS) are a common cause of leg pain in athletes. Shin splints are a result of connective muscle tissue in the lower leg becoming inflamed and causing pain. Shin splints that are left untreated for a long period of time can progress to tibial stress fractures.
What causes Shin Splints?
Factors that can contribute to the development of shin splints include:
-
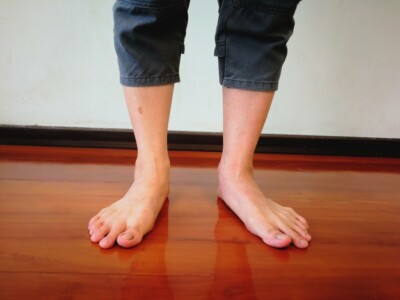
- Tightness in the calf muscles (this can cause further pronation)
- Over-pronation causes the tibia to twist and the muscles in the lower leg to overstretch
- Muscle weakness, particularly of the tibialis anterior and tibialis posterior muscles
- Increasing intensity and duration of activity too quickly (beginner runners are particularly prone to shin splints)
- Improper or ‘worn-out’ footwear
- Running on inclines, uneven terrain or hard surfaces
How do I know if I have Shin Splints?
If you have shin splints you will usually feel pain or tenderness on the inside of the shin (medial) or on the front of the shin (anterior). If you are a runner, you will probably notice pain is worst at the start of a run and may disappear during the run as your muscles loosen up. However, in more severe cases, the pain may not ease and you may also notice symptoms during other weight-bearing activities such as walking and climbing stairs.
What is the treatment for shin splints?
It is important to get a gait analysis done by a podiatrist. A Bio-mechanical Assessment will ascertain whether your foot function has played a role in acquiring this injury. The initial treatment for shin splints is rest. If you are a runner, it is recommended that you either cease or reduce your running distance and intensity, or alternatively change your mode of exercise, ie cycling or swimming. Ice and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication can also assist in reducing inflammation. Appropriate and supportive footwear is also important and a podiatrist will be able to advise on the best footwear to suit your foot type. Orthotics may also be recommended if greater foot motion control is required.
Book a Podiatry Appointment
OTHER CONDITIONS WE TREAT
What our clients say